Impedance Measurement Body Fat
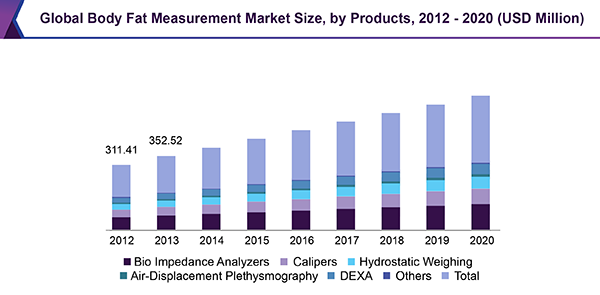
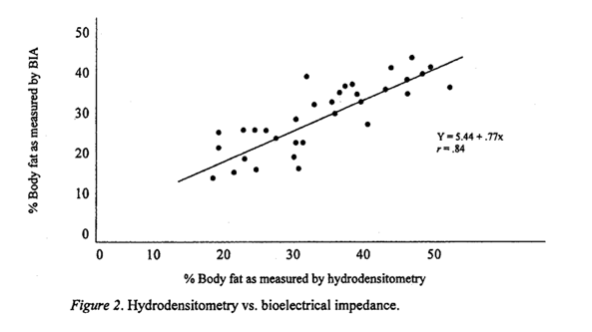
In part 1 of this series you learned about how body fat testing is a prediction not a measurement. Bia or bioelectrical impedance analysis is a non invasive measurement of body fat lean muscle mass and hydration. While not as accurate as skinfold measurements taken by a trained. Now lets talk about bia. Since the advent of the first commercially available devices. In part 2 you learned about underwater weighing and in part 3 you learned about the bod pod.
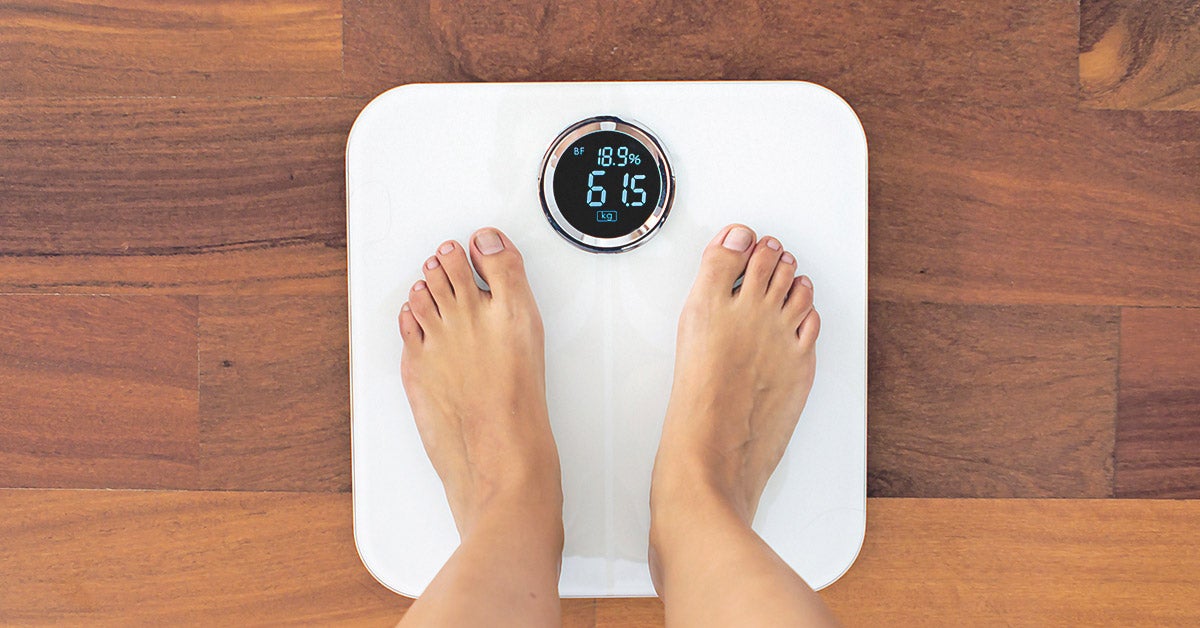
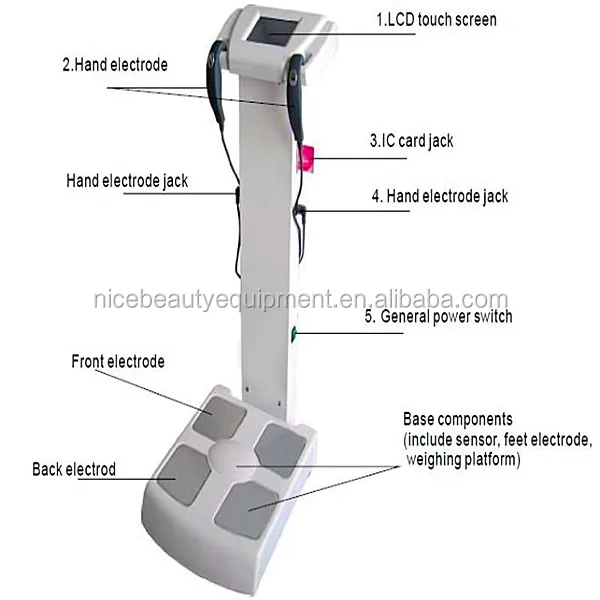
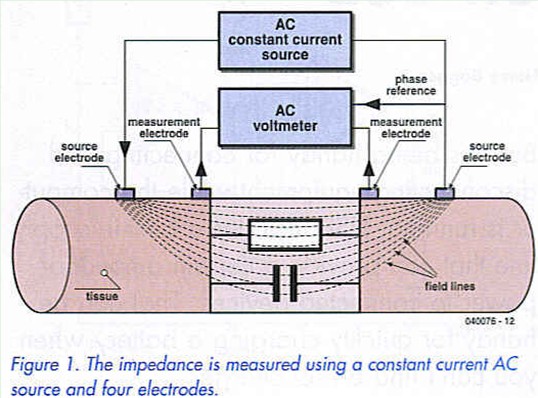
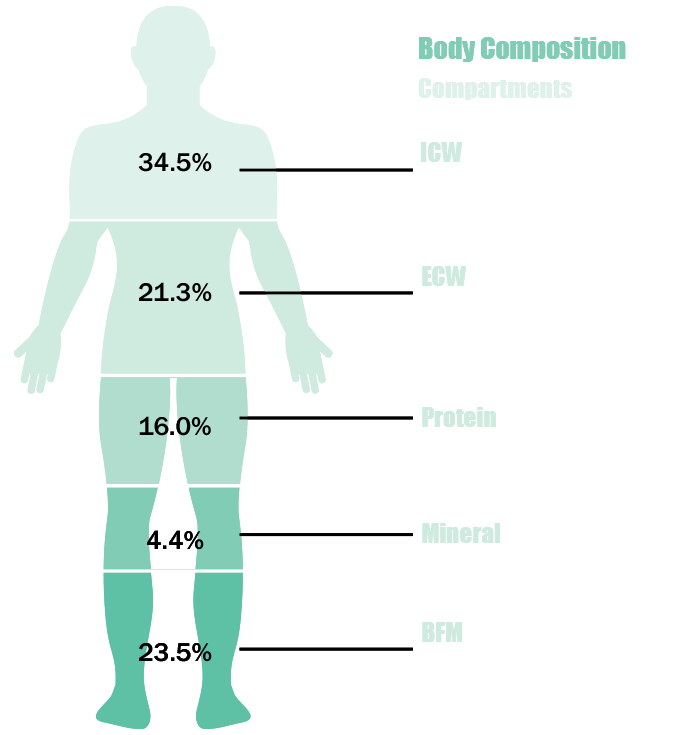
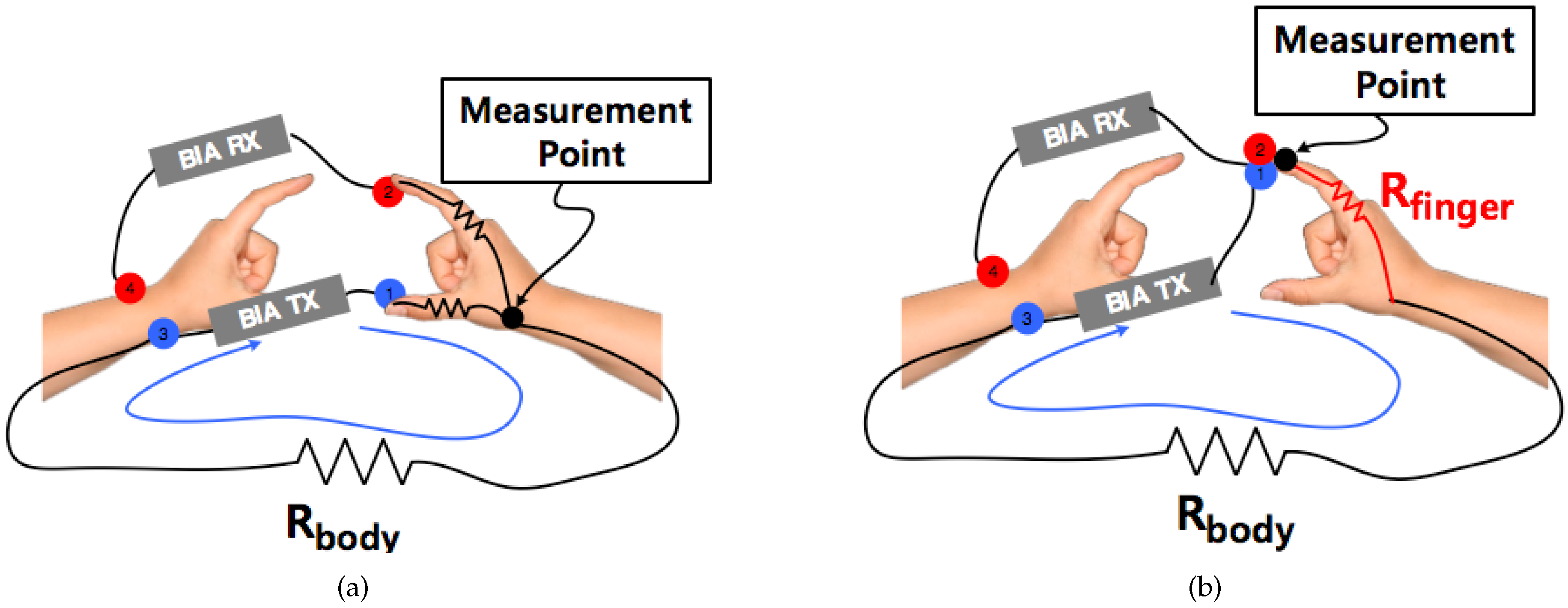
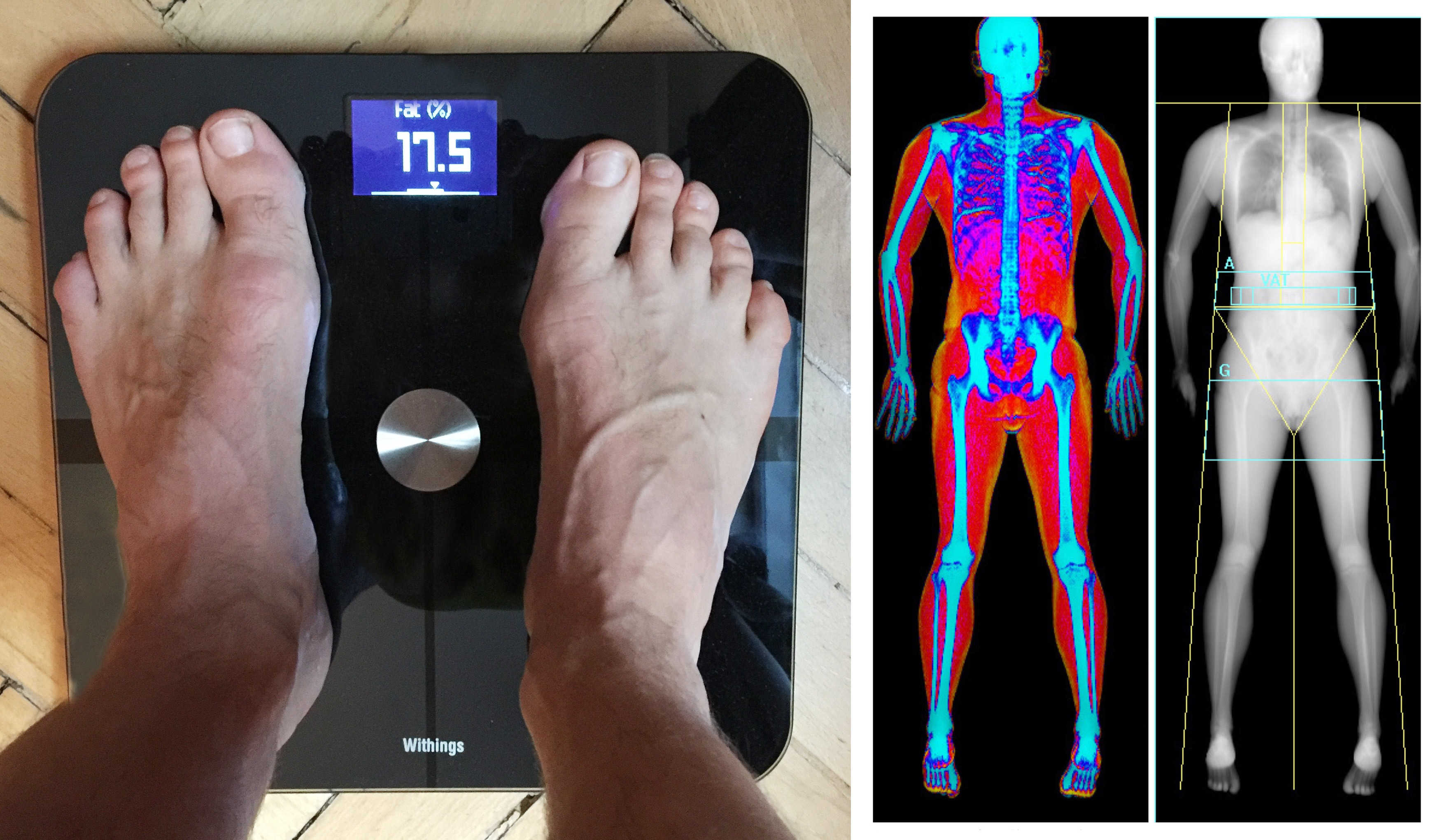
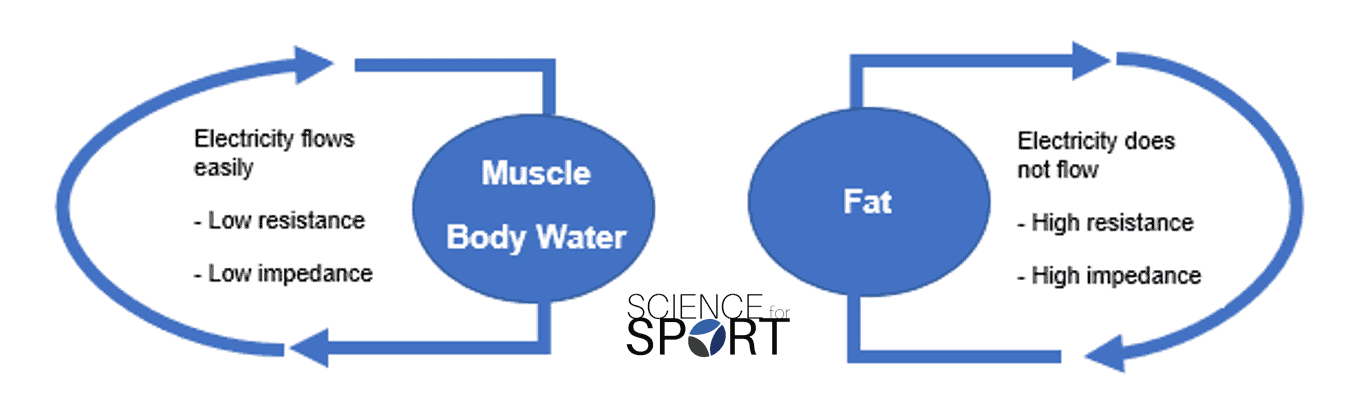
In bia a weak electric current flows through the body and the voltage is measured in order to calculate impedance of the body. Therefore if a person is more muscular there is a high chance that the person will also have more body water which leads to lower impedance. Most body water is stored in muscle. Bia sends a weak electrical impulse through the. However the convienience of this method comes at a price of accuracy. When you step on the scale a small electrical current runs up through your leg and across your.
Body circumference measurements and body fat scales that use bioelectrical impedance are both methods you can do on your own. Bioelectrical impedance analysis is a commonly used method for estimating body composition in particular body fat and muscle mass. Such scales work with the help of sensors underneath your feet that use bioelectrical impedance. Bioelectrical impedance bia bia is one of the quickest and easiest methods for predicting body fat. A small current is used to measure the resistance at difference frequencies against the various tissues in the body eg fatlipid has a high resistance to the flow of current therefore shows a high impedance reading. Body fat scales use bioelectrical impedance analysis bia to estimate the relative percentages of different tissues and substances within the body.
Random Post
- pancreatic body measurements
- aman hundal body measurement
- how to take body measurement for salwar kameez
- boux avenue bra measurement
- virat kohli body measurement
- pure neemo body measurements
- sumeet sahni body measurements
- skinfold measurement technique for determining body fat
- yuvika chaudhary body measurement
- method of body measurement
- body measurement hayley orrantia
- body temperature measurement pdf
- juhi rustagi body measurement
- saira banu body measurements
- carrie keagan body measurement
- body measurement units
- body measurement chart beachbody
- jodi lyn o'keefe body measurement
- sanne vloet body measurement
- body mass measurement device
- ab de villiers body measurements
- body measurement cgv
- tobey maguire body measurements
- body measurement kirsten powers
- undertaker body measurement
- nba players body measurements
- body fluid measurement
- how to measure body measurement
- sheamus body measurements
- body measurement catherine zeta jones
- elli avram body measurement
- enter body measurements see shape
- siddharth desai body measurement
- genevieve nnaji body measurement
- which statement is true about body temperature measurement in rodents
- meenakshi joshi body measurement
- body dimensions gym
- kiernan shipka body measurement
- bridgette wilson body measurement
- greek body measurement
- what do my body measurements say about me
- lena meyer landrut body measurement
- how to do body measurements female
- cool body measurement facts
- bhojpuri actress body measurements
- under bra measurement
- body measurement names
- alisha panwar body measurement
- rib measurement bra size
- parth samthaan body measurement